Market Overview
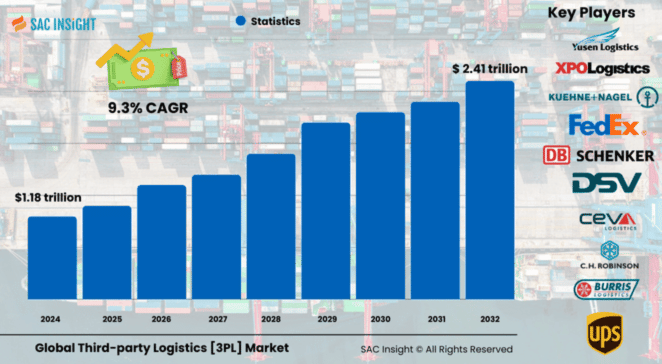
The Global third-party logistics [3PL] market size was valued at US$ 1.18 trillion in 2024 and is projected to reach roughly US$ 2.41 trillion by 2032, registering a 9.3% CAGR over the forecast period. This market growth is propelled by the boom in cross-border e-commerce, the push for last-mile efficiency, and a steady shift from fixed-asset fleets to asset-light, technology-rich logistics partnerships. First-hand industry insights show manufacturers and retailers alike moving from multi-warehouse models to centralized hubs supported by real-time visibility tools. SAC Insight evaluation also highlights robust U.S. momentum—the U.S. 3PL market size is on track to top about US$ 590 billion by 2032 as near-shoring and cold-chain demand accelerate.
Summary of Market Trends & Drivers
• Last-mile delivery is moving from “two-day” to “same-day,” driving investment in micro-fulfillment, route optimization, and smaller urban vehicles.
• AI-powered transport management systems (TMS), predictive analytics, and blockchain track-and-trace are becoming baseline requirements rather than nice-to-haves.
• Shippers are increasingly outsourcing complex customs, sustainability reporting, and reverse-logistics tasks, expanding the scope of traditional 3PL contracts.
Key Market Players
The third-party logistics market report covers global and regional leaders such as C.H. Robinson, DHL Group, Kuehne + Nagel, FedEx, UPS, DB Schenker, Nippon Express, XPO Logistics, DSV, and CEVA Logistics. These companies set the competitive pace through dedicated contract carriage, integrated freight-forwarding networks, and heavy investment in automation and robotics. A rising cohort of tech-native challengers—often backed by private equity—are leveraging digital freight marketplaces and asset-light models to win share in niche lanes.
Key Takeaways
• Market value (2024): US$ 1.18 trillion
• Projected value (2032): US$ 2.41 trillion at a 9.3% CAGR
• Road transport retains the largest market share (~58%), but air freight is the fastest-growing mode.
• Domestic Transportation Management remains the biggest service slice, yet International Transportation Management shows double-digit expansion on the back of new free-trade pacts.
• Asia-Pacific commands ~46% of revenue and is also the quickest-growing region.
• Advanced robotics, AI route planning, and warehouse management systems are the standout market trends shaping competitive advantage.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
• Explosive e-commerce volumes demanding faster, cheaper fulfillment.
• Globalization of SME supply chains needing turnkey customs and compliance support.
• Adoption of cloud-based TMS/WMS delivering 20-30% efficiency gains.
Restraints
• Infrastructure gaps and road congestion in emerging markets.
• Shortage of skilled logistics professionals to run advanced systems.
• Patchwork regulatory frameworks that add cost and complexity.
Opportunities
• Growth of 4PL and control-tower services offering end-to-end orchestration.
• Green logistics—electrified fleets, modal shifts, and carbon-tracking dashboards—opening premium service niches.
• Rising healthcare and cold-chain requirements creating high-margin lanes.
Challenges
• Tight trucking capacity and driver shortages in North America and Europe.
• Cyber-security risks as data-rich supply chains become prime hacker targets.
• Margin pressure from shippers demanding rate transparency and dynamic pricing.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific dominates thanks to dense manufacturing corridors, surging digital retail, and heavy investment in road, rail, and port upgrades. North America follows, buoyed by near-shoring and cold-chain projects, while Europe’s emphasis on sustainability standards is reshaping fleet choices.
• Asia-Pacific: E-commerce hubs in China, India, and Southeast Asia drive double-digit market growth.
• North America: Near-shoring and cold-storage expansion underpin steady gains.
• Europe: Green-logistics mandates and truck-platooning pilots support technology uptake.
• Latin America: Trade-lane diversification and free-trade zones spur incremental demand.
• Middle East & Africa: Infrastructure corridors and port investments lay groundwork for future scale.
Segmentation Analysis
By Service
• Dedicated Contract Carriage (DCC) – guaranteed capacity, predictable cost.
DCC lets shippers offload fleet ownership while retaining brand-specific trucks and drivers—ideal for high-volume retailers.
• Domestic Transportation Management (DTM) – largest revenue slice.
DTM covers in-country freight brokerage, routing, and cross-docking. Rising fuel surcharges and dynamic pricing tools make this segment a critical cost lever.
• International Transportation Management (ITM) – fastest globalizer.
ITM services manage cross-border moves, customs, and documentation; recent trade-agreement expansions fuel its rapid climb.
• Warehousing & Distribution – pivot to omnichannel fulfillment.
Automation, micro-fulfillment, and temperature-controlled storage keep this segment essential for perishable and high-velocity SKUs.
• Value-Added Logistics Services (VALs) – competitive differentiator.
Kitting, labeling, reverse logistics, and light assembly help shippers delay product configuration and cut inventory.
By Transport Mode
• Roadways – backbone, >58% share.
High flexibility and improved highway networks keep road freight the default for domestic moves.
• Railways – cost-efficient bulk and long haul.
Sustained investment in intermodal hubs makes rail attractive for heavy industrial cargo.
• Waterways – economical for heavy, non-urgent freight.
Deep-water port upgrades in Asia and the Middle East boost container throughput.
• Airways – premium, 9%+ CAGR.
Post-pandemic medical and high-tech shipments sustain air-freight momentum despite higher rates.
By End-use
• Manufacturing – 25% share, complex multi-tier supply chains.
Just-in-time production relies on visibility and synchronized inbound flows.
• Retail & E-commerce – fastest-growing end-use.
Omnichannel strategies demand scalable, returns-friendly networks.
• Automotive – pivot to EV parts logistics.
Battery transport regulations and sequencing centers raise service sophistication.
• Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals – strict temperature and compliance needs.
GDP-compliant cold chains expand as biologics and vaccines proliferate.
• Others – including food & beverage, high-tech, and consumer electronics.
Each sub-sector seeks tailored 3PL solutions to balance speed, cost, and risk.
Industry Developments & Instances
• Feb 2024: DHL rolled out resale-logistics services via a partnership with a circular-commerce platform, expanding into reverse supply chains.
• Jan 2024: C.H. Robinson launched electronic bills of lading with 10 major LTL carriers, boosting real-time visibility.
• Nov 2023: DHL deployed 1,000 AutoStore robots, underscoring the march toward lights-out warehouses.
• Jul 2023: Maersk opened its first UAE cold-store facility, strengthening Middle East perishables flows.
• Jun 2023: DHL Supply Chain signed a multi-year healthcare 3PL contract covering spare-part logistics and field inventory.
Facts & Figures
• Last-mile deliveries now account for ~53% of total parcel-delivery cost.
• AI-enabled route optimization can cut fuel spend by up to 15%.
• Road freight spot rates in the U.S. climbed 11% year-on-year in 2024.
• 46% of shippers plan to increase 3PL outsourcing over the next two years.
• Automated warehouses can raise order-pick accuracy to 99.7%, trimming returns and write-offs.
Analyst Review & Recommendations
SAC Insight analysis indicates the 3PL Market is shifting from capacity brokerage to technology-driven orchestration. Providers that pair robust carrier networks with AI-powered control towers, sustainability dashboards, and flexible value-added services will outpace peers. Shippers should prioritize partners offering end-to-end data visibility and demonstrable emissions-reduction roadmaps, while 3PLs must invest in talent and cyber-security to safeguard expanding digital ecosystems.






