Market Overview
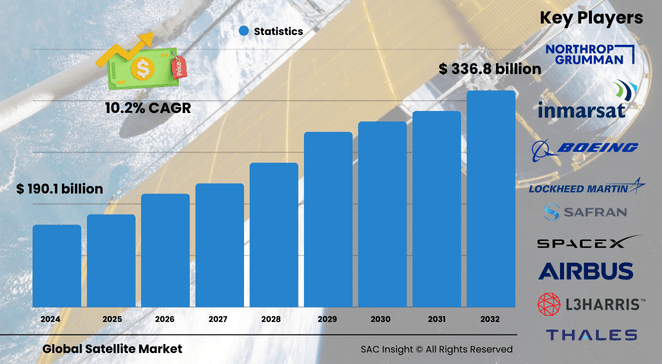
The global satellite market size stood at approximately US$ 190.11 billion in 2024 and is forecast to reach about US$ 336.87 billion by 2032, reflecting a 10.2% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) during 2025-2032. Robust demand for always-on connectivity, surging launches of low-Earth-orbit (LEO) broadband constellations, and a steady rise in government spending on space-based positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) are driving sustained market growth.
The U.S. satellite market is projected to expand from US$ 96.63 billion in 2024 to about US$ 220.86 billion by 2032, on the back of defense modernization and aggressive LEO roll-outs.
Market Trends & Drivers
• Explosive appetite for satellite-based broadband and IoT backhaul is reshaping constellation economics and shortening replacement cycles.
• Governments are prioritizing resilient PNT and secure communications, leading to multi-year procurement pipelines and technology refresh programs.
• Advances in electric propulsion, green propellants, and reusable launch systems are cutting costs per kilogram and accelerating time to orbit.
Key Market Players
SpaceX, Lockheed Martin, Airbus Defence & Space, Northrop Grumman, and Thales Alenia Space anchor the competitive landscape with vertically integrated launch, bus, and payload capabilities. Close behind are L3Harris, Maxar, Mitsubishi Electric, Planet Labs, York Space Systems, and a wave of small-sat specialists that focus on rapid manufacturing and data analytics.
Key Takeaways
• Global market value (2024): USD$ 190.11 billion
• Projected value (2032): USD$ 336.87 billion at a 10.2% CAGR
• North America commands about 37% market share, with Asia-Pacific as the fastest-growing region
• Large satellites remain critical for high-capacity communications; small satellites post the highest unit growth
• Commercial communications lead revenue, but Earth observation and PNT are closing the gap
• Nearly 5,000 satellites are expected to launch annually by the end of the decade, intensifying capacity and debris management pressures
Market Dynamics
Drivers
• Escalating demand for high-throughput connectivity in remote and underserved regions
• Rising defense and homeland-security budgets for secure, sovereign space assets
• Technological advances in miniaturization, electric propulsion, and reusable rockets that lower launch costs
Restraints
• High upfront investment for constellation deployment and in-orbit servicing infrastructure
• Limited individual satellite coverage necessitating large fleets and complex coordination
• Spectrum allocation challenges as multiple players crowd popular Ku- and Ka-band frequencies
Opportunities
• Satellite-enabled data analytics for agriculture, insurance, and disaster response open new revenue streams
• Growing funding pipelines for green propulsion and active debris removal technologies
• Public–private partnerships in emerging economies to bridge the digital divide with LEO broadband
Challenges
• Rapidly increasing space debris elevates collision risk and raises insurance premiums
• Supply-chain constraints for radiation-hardened semiconductors and specialty alloys
• Regulatory uncertainty around orbital rights, spectrum sharing, and in-orbit servicing protocols
Regional Analysis
North America leads the market on the strength of sustained federal spending, an established launch ecosystem, and an active commercial space sector. Asia-Pacific is posting double-digit gains as China, India, Japan, and South Korea fund national constellations and smart-city initiatives, while Europe’s focus on environmental monitoring and green propulsion keeps it technologically competitive.
• North America – Largest revenue pool; driven by defense modernization and LEO megaconstellations
• Europe – Accelerating investment in green propulsion and climate-monitoring missions
• Asia-Pacific – Fastest CAGR; significant government backing and smart-city demand
• Latin America – Early-stage adoption with emphasis on connectivity for rural regions
• Middle East & Africa – Rising interest in Earth-observation data for resource management and security
Segmentation Analysis
By Satellite Mass
• Large Satellites – Backbone of high-capacity networks
Large platforms deliver superior payload power and bandwidth, underpinning national security communications and weather forecasting.
• Medium Satellites – Flexible workhorses
Mid-class buses balance performance with lower launch costs, making them attractive for regional broadcast and navigation augmentation missions.
• Small Satellites – Fastest-growing volume segment
CubeSats and microsats enable rapid technology refresh, low-cost experimentation, and dense imaging revisit rates.
By Orbit
• Low Earth Orbit (LEO) – High-density constellation hub
LEO’s latency advantage fuels broadband and sensing applications.
• Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) – Navigation stronghold
MEO remains vital for global navigation systems and emerging hybrid communications architectures that blend latency and coverage.
• Geostationary Orbit (GEO) – Strategic high-throughput layer
GEO satellites continue to deliver persistent coverage for broadcast, backhaul, and national security, even as operators adopt flexible digital payloads to stay competitive.
• High-Altitude/Other Orbits – Niche science and HAPS
Highly elliptical and high-altitude platform systems serve specialized polar, deep-space, and stratospheric missions, carving out small but strategic niches.
By Application
• Commercial Communications – Core revenue engine
Growing video streaming, enterprise-connectivity, and backhaul needs cement this segment’s lead.
• Earth Observation & Remote Sensing – Rapid uptake
High-resolution imaging and data-fusion services cater to agriculture, insurance, and climate monitoring.
• Navigation & PNT – Strategic priority
Precise location and timing underpin everything from financial trading to autonomous vehicles.
• Science & Exploration – Technology incubator
Space agencies and consortiums leverage bespoke satellites for astronomy, heliophysics, and lunar gateway support, driving innovation with spill-over benefits to commercial markets.
By End-User
• Government & Civil – Largest spending block
Budgets target national security, disaster response, and digital inclusion, sustaining long-term procurement pipelines.
• Military – High-specification demand
Secure, anti-jam communications, missile warning, and tactical ISR require hardened satellites and classified payloads.
• Commercial – Entrepreneurial growth frontier
Telecom operators, analytics firms, and new-space start-ups spearhead constellation roll-outs and data-as-a-service models.
Industry Developments & Recent Market Developments
• October 2023 – A major launch provider secured a USD$ 70 million contract to deploy dedicated broadband satellites for a defense customer.
• January 2024 – A defense prime won an USD$ 890 million order to build 18 missile-tracking satellites for a next-generation warning layer.
• January 2024 – A leading aerospace group became sole owner of a U.S. satellite factory to streamline serial production for commercial and institutional buyers.
• October 2024 – A flagship data-transport constellation added 38 cross-link satellites through a contract with a heritage defense integrator.
• October 2024 – A European space agency ordered six Earth-observation spacecraft to expand a regional environmental-monitoring program.
• October 2022 – A heavy-lift launch vehicle from South Asia orbited 36 broadband satellites for an international operator, marking a milestone in commercial rideshare.
• February 2023 – A hybrid-orbit communications satellite reached GEO, enhancing dual L-band and Ka-band service coverage.
• September 2022 – A domestic broadband provider activated the country’s first high-throughput satellite network, extending coverage to underserved rural zones.
Facts & Figures
• Roughly 3,154 satellites launched in 2024; annual launches expected to top 5,000 by 2030.
• Average constellation replacement cycle is shortening to 5-7 years as operators pursue fresher technology.
• Space agencies estimate more than 150 million debris objects orbiting between LEO and GEO, weighing over 5,000 tons.
• About 37% of global revenue originated in North America in 2024, while Asia-Pacific posted the quickest double-digit gains.
• Green propulsion systems could cut in-orbit fuel mass by up to 40%, freeing room for higher-value payloads.
• Large satellites are on track to generate USD$ 19.71 billion in revenue by 2032, even as small satellites dominate unit counts.
Analyst Review & Recommendations
SAC Insight's deep market evaluation underscores a dual-track future: high-capacity GEO and medium-class platforms will coexist with proliferated LEO fleets optimized for low latency and rapid refresh. Operators that pair flexible digital payloads with cloud-native ground infrastructure will capture outsized share as capacity pricing tightens. Investors should watch suppliers of electric propulsion, active debris removal, and on-orbit servicing for breakout growth. Maintaining trust with regulators through transparent debris-mitigation plans will be just as critical as lowering launch costs in sustaining long-term market expansion.






