Market Overview
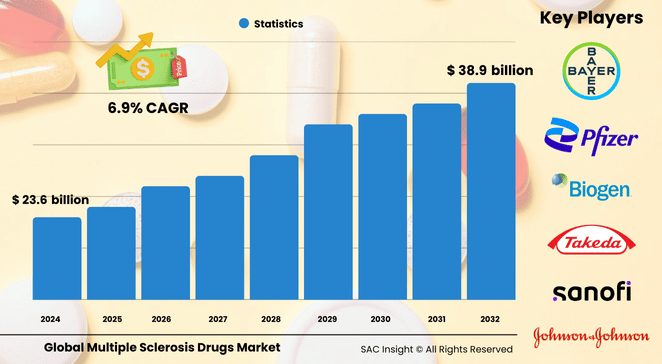
The global multiple sclerosis drugs market size is valued at roughly US$ 23.64 billion in 2024 and is set to climb to about US$ 38.94 billion by 2032, advancing at a 6.9% CAGR during 2025-2032. Historical market analysis covering 2020-2023 shows an average market value of US$ 23.64 billion, reflecting steady post-pandemic recovery as treatment volumes normalize. SAC insights point to three structural tailwinds: a rising diagnosed population (2.9 million people in 2023 versus 2.3 million in 2013), a pivot toward high-efficacy disease-modifying therapies, and government-backed awareness campaigns that encourage early intervention.
SAC Insight's deep market evaluation also indicates a healthy U.S. pipeline; the U.S. multiple sclerosis (MS) drugs market alone is on track to reach nearly US$ 13.6 billion by 2032, underscoring North America’s outsize influence.
Summary of Market Trends & Drivers
Demand is shifting toward monoclonal-antibody and next-generation oral agents as clinicians target earlier, more aggressive disease control. At the same time, payers in Europe and Asia are expanding reimbursement for biosimilars, widening access and putting price pressure on legacy brands. Digital adherence apps, wearable symptom trackers, and remote infusion monitoring are further shaping market trends by improving patient compliance and supporting value-based care models.
Key Market Players
Global multiple sclerosis drugs market leadership rests with a handful of companies that combine proven portfolios with active late-stage pipelines. Biogen and F. Hoffmann-La Roche anchor the high-efficacy segment with blockbuster therapies, while Novartis, Sanofi, and Merck leverage broad neurology franchises to defend market share across drug classes. Teva Pharmaceutical Industries and Pfizer push affordability through generics and biosimilars, and Bayer AG, Johnson & Johnson, Takeda, and Horizon Therapeutics round out the competitive landscape with focused innovation or regional scale. Together, these firms drive market growth through rapid label expansions, strategic licensing, and real-world evidence programs that bolster prescriber confidence.
Key Takeaways
• 2024 market value: USD$ 23.64 billion
• 2032 projection: USD$ 38.94 billion at a 6.9% CAGR (2025-2032)
• North America holds roughly 43.25% market share, led by the U.S.
• Immunosuppressants command 60.8% of revenue; injectables represent 52.9% of all sales
• Oral disease-modifying therapies show the fastest segment growth (7% CAGR)
• Monoclonal antibodies, biosimilars, and digital adherence platforms are the top technology catalysts
Market Dynamics
Drivers
• Rising prevalence and earlier diagnosis fuel consistent therapy uptake
• Strong R&D investment delivers next-generation antibodies and BTK inhibitors
• Government initiatives and patient-advocacy campaigns expand treatment access
Restraints
• High annual drug costs—median near USD$ 94,000—limit broad adoption
• Payer-driven step-therapy and prior-authorization hurdles delay initiation
• Supply-chain complexity for biologics raises distribution costs in emerging markets
Opportunities
• Biosimilar launches open price-sensitive segments and promote wider coverage
• Companion digital therapeutics improve adherence and data-rich care pathways
• Precision-immunology pipelines target remyelination, a potential paradigm shift
Challenges
• Intensifying competition pressures margins, especially for first-generation injectables
• Ongoing safety monitoring for long-acting antibodies demands significant post-market resources
• Workforce gaps in neurology and infusion services could constrain real-world capacity
Regional Analysis
North America dominates thanks to advanced diagnostics, favorable reimbursement, and aggressive drug launches. Europe follows, supported by robust healthcare funding and proactive treatment guidelines, while Asia-Pacific registers the fastest expansion as China and India strengthen neurological care networks.
• North America – Largest market; innovation hub and early adopter of premium biologics
• Europe – Strong guideline alignment, high treatment penetration, pressure for cost-effectiveness
• Asia-Pacific – Double-digit growth driven by expanding insurance coverage and local manufacturing
• Latin America – Gradual uptake, aided by biosimilar introduction and public-sector tenders
• Middle East & Africa – Emerging access programs and specialty-pharmacy investments support steady gains
Segmentation Analysis
By Drug Class
• Immunosuppressants – 60.8% share, backbone of modern MS therapy
Immunosuppressants dampen aberrant immune activity and remain the first choice for rapidly controlling relapses and disability progression. Steady clinical data and physician familiarity keep these agents in pole position.
• Immunomodulators – High clinician uptake, pivotal in long-term maintenance
These drugs fine-tune immune responses rather than blunt them outright, offering balanced efficacy and tolerability that sustain their popularity in newly diagnosed cohorts.
• Interferons – Established workhorses facing biosimilar competition
Long on safety and real-world evidence, interferons still anchor many treatment algorithms, though price erosion and newer options are eroding growth.
• Others (Monoclonal antibodies and emerging mechanisms) – Fast-growing niche
Next-wave antibodies and BTK inhibitors promise potent disease control and convenient dosing, positioning this segment for above-average expansion through 2032.
By Route of Administration
• Injectable – 52.9% share, valued for rapid onset and proven outcomes
Subcutaneous and intravenous products dominate hospital infusion suites and at-home self-injection programs, maintaining a central role in relapse prevention. Injectables deliver quick bioavailability and clinician confidence, though convenience concerns and needle fatigue keep demand for alternatives high.
• Oral – Roughly 7% CAGR, preferred for ease of use
Patient-friendly dosing schedules and fewer clinic visits drive robust uptake, especially for front-line therapy in mild-to-moderate disease. Once-daily capsules lower treatment burden, spurring adherence and opening opportunities in markets with limited infusion infrastructure.
• Others (e.g., implantable, transdermal) – Experimental but intriguing
Novel delivery modes aim to improve steady-state dosing and minimize systemic exposure, though most remain at the proof-of-concept stage.
By Distribution Channel
• Hospital Pharmacy – 46.8% share, hub for complex infusion and monitoring
Centralized inventory and reimbursement processing make hospitals the primary outlet for high-cost biologics.
• Retail Pharmacy – Growing at 6.4% as convenience drives refills
Expanded pharmacist authority and patient-support services help shift chronic oral therapies into community settings.
• Online/E-commerce – Rapidly scaling specialty platforms
Mail-order and digital-first pharmacies enhance adherence programs and deliver cost transparency, appealing to tech-savvy patients.
Industry Developments & Instances
• February 2024 – Roche launched Ocrevus in India, expanding access to primary progressive and relapsing MS patients.
• February 2024 – Neuraxpharm introduced Briumvi across Europe for adult relapsing MS.
• August 2023 – The U.S. FDA cleared Tyruko, the first biosimilar of Tysabri, opening a lower-cost pathway in relapsing disease forms.
• April 2021 – Biogen secured EU approval for subcutaneous Tysabri, offering quicker administration in clinic or at home.
• July 2021 – Biogen and InnoCare signed a global license for orelabrutinib, strengthening the BTK inhibitor pipeline.
Facts & Figures
• 2.9 million people globally live with MS, up 26% since 2013.
• Immunosuppressants hold 60.8% of global revenue; injectables account for 52.9% of volume.
• North America commands roughly 43.25% of market size; the U.S. contributes 80.8% of regional sales.
• Median annual disease-modifying therapy cost is about USD$ 94,000 in developed markets.
• Monoclonal antibodies generated over USD$ 7 billion in global revenue in 2024, growing double digits year-over-year.
Analyst Review & Recommendations
Market growth will hinge on balancing innovation with affordability. Companies that pair high-efficacy antibodies or BTK inhibitors with evidence-led pharmacoeconomic data will resonate with payers, while biosimilar strategies can defend volume in price-sensitive segments. Strengthening digital adherence tools and infusion-capacity partnerships will differentiate brands as patient loads climb. Overall, sustained R&D momentum and proactive access programs should keep the multiple sclerosis drugs market on a steady upward trajectory through 2032.






