Market Overview
The global industrial robotics market size was valued at approximately US$ 26.92 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach about US$ 57 billion by 2032, reflecting a robust 12.05% CAGR over the 2025-2032 forecast window. First-hand industry insights highlight three structural growth engines: relentless e-commerce expansion demanding faster fulfilment, rising labour shortages across high-skill manufacturing, and a decisive shift toward data-driven, AI-enabled automation.
SAC Insight's deep market evaluation indicates that Asia Pacific already controls nearly half of global market share (48.72% in 2024) while North America, though smaller at 8%, is accelerating investments in reshoring and smart factories. The U.S. industrial robotics market alone is set to top roughly US$ 7.61 billion by 2032 thanks to logistics, healthcare, and automotive upgrades.
Summary of Market Trends and Drivers
• Robots-as-a-Service (RaaS) subscription models are lowering upfront costs, opening the door for small and mid-sized enterprises to adopt automation on an operating-expense basis.
• Collaborative robots (cobots) with advanced vision and safety sensors are working side-by-side with employees, improving productivity without heavy guarding.
• Sustainability mandates are pushing manufacturers toward energy-efficient robotics that minimize material waste and support closed-loop production.
Key Takeaways
• Global industrial robotics market value (2024): USD$ 26.92 billion
• Projected value (2032): USD$ 57 billion at a 12.05% CAGR
• Handling/material-handling applications command 42% of 2024 revenue thanks to heavy-payload demand in automotive and aerospace.
• Asia Pacific leads with nearly 49% market share; China, Japan, and South Korea remain the epicentre of robot installations.
• RaaS offerings, cobots under 16 kg payload, and AI-powered inspection are the fastest-growing niches.
• U.S. reshoring and European green-manufacturing incentives are creating fresh pockets of market growth.
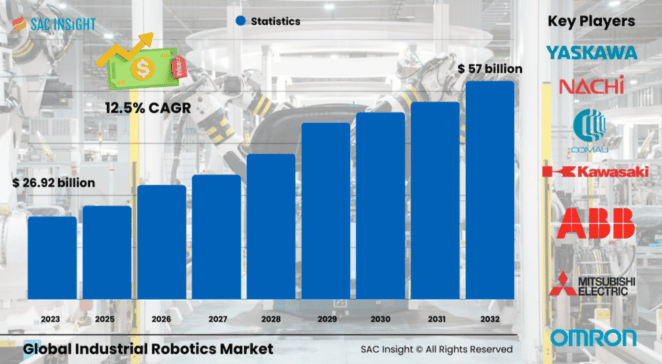
Key Market Players
Global leadership is shaped by diversified automation groups such as ABB, Fanuc, Yaskawa, KUKA, and Mitsubishi Electric. These firms bundle hardware with AI-driven controllers, predictive-maintenance software, and IIoT connectivity to lock in recurring revenue streams and deepen customer stickiness. A dynamic second tier—including Denso, Omron, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, and emerging cobot specialists—focuses on niche payload ranges, sector-specific end-effectors, and modular platforms. Their strategy revolves around rapid product refreshes, local partnerships, and targeted M&A that sharpen regional competitiveness while extending global reach.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
• Surge in smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 adoption across automotive, electronics, and logistics.
• Rising e-commerce volume requiring automated sorting, picking, and last-mile solutions.
• Continuous cost decline in sensors, edge computing, and AI chips boosting performance-to-price ratios.
Restraints
• High initial capital plus integration and maintenance costs, particularly for SMEs outside RaaS models.
• Shortage of skilled robotics engineers and integrators slowing large-scale deployments.
Opportunities
• Expanding adoption in emerging economies as governments subsidise factory automation.
• Healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors embracing sterile, high-precision robots for lab automation and drug packaging.
• Sustainability pressure driving demand for low-energy, recyclable robot components.
Challenges
• Cybersecurity risks linked to always-connected IIoT architectures.
• Complex, evolving safety regulations that demand ongoing certification and compliance investment.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific dominates due to rapid industrialisation, sizeable electronics and automotive clusters, and supportive national robotics initiatives. North America is gaining momentum through reshoring and logistics automation, while Europe leans on cobot uptake and strict green-manufacturing standards.
• Asia Pacific – Largest market, fastest installation rates, strong government incentives.
• North America – Growth driven by logistics, healthcare, and domestic manufacturing revival.
• Europe – Sustainability and collaborative safety standards foster cobot leadership.
• Latin America – Moderate expansion tied to automotive and food-processing investments.
• Middle East & Africa – Early-stage adoption, focused on oil & gas maintenance and new manufacturing hubs.
Segmentation Analysis
By Application
• Handling – Cornerstone segment with 42% revenue share
High-payload robots streamline lifting, palletising, and warehouse tasks, cutting manual-handling injuries and cycle times.
• Welding & Soldering – Precision critical for automotive bodies and electronics boards
Arc-welding arms equipped with vision guidance deliver repeatable seams and lower defect rates.
• Assembling & Disassembling – Growing with electronics miniaturisation
Six-axis units place micro-components accurately, supporting faster line changeovers.
• Processing – Rapid rise in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical lines
Hygienic robots slice, mix, and package under strict contamination controls, meeting global safety standards.
• Others (Dispensing, Cleanroom, Inspection) – Specialised tasks demanding accuracy and speed
Targeted niches include semiconductor wafer handling and battery cell inspection.
By Robot Type
• Articulated – Versatile workhorse spanning 6-axis flexibility
Ideal for complex motions from painting car bodies to loading CNC machines.
• SCARA – High-speed pick-and-place specialist
Dominant in electronics and light-assembly lines requiring horizontal precision.
• Cartesian/Linear – Customisable for large work envelopes
Widely used in palletising and additive-manufacturing gantries.
• Cylindrical, Parallel, Delta, Others – Niche options for compact footprints or ultra-fast throughput
Each addresses specific speed, reach, or cost constraints in packaging and small-part assembly.
By Payload Capacity
• Up to 16 kg – Fastest-growing cobot class
Lightweight arms suit electronics, lab automation, and high-mix assembly.
• 16–60 kg – General-purpose range for automotive sub-assemblies and welding
Balances reach, speed, and moderate payloads for diversified factories.
• 61–225 kg – Heavy-duty performers
Handle car chassis, engine blocks, and sheet-metal panels with high precision.
• Above 225 kg – Ultra-heavy material movers
Serve foundries, aerospace, and shipbuilding where human handling is impractical.
By Industry
• Automotive – Largest adopter, leveraging robots for body-in-white, painting, and battery pack assembly.
• Electrical & Electronics – High-precision soldering, PCB handling, and cleanroom operations.
• Healthcare & Pharmaceutical – Rapid growth in sterile packaging, lab diagnostics, and hospital logistics.
• Food & Beverages – Robotic slicing, packing, and quality inspection under hygiene mandates.
• Metals & Machinery, Rubber & Plastics, Construction, Logistics – Expanding adoption for hazardous or repetitive tasks.
Industry Developments and Instances
• May 2024 – Neura Robotics partnered with Omron to roll out AI-enhanced cognitive robots for safer, smarter factories.
• February 2024 – Olis Robotics and Kawasaki introduced remote error-recovery tech cutting downtime by up to 90%.
• June 2024 – RoboDK and KEBA Industrial Automation integrated simulation tools, streamlining robot-cell commissioning.
• September 2024 – KUKA unveiled a 60 kg-payload SCARA unit targeting pharma and EV battery lines.
• March 2024 – Universal Robots joined forces with NVIDIA to infuse edge-AI into next-gen cobots.
Facts & Figures
• Roughly 600 thousand new industrial robots were installed worldwide in 2023, up 12% year-on-year.
• Cobots under 16 kg payload recorded a 22% shipment jump in 2024 amid SME demand.
• RaaS contracts now represent about 15% of new robot deployments, triple the share in 2021.
• AI-enabled visual inspection cuts defect rates in electronics plants by up to 40%.
• Precision-guided welding arms can reduce scrap in automotive body shops by nearly 25%.
Analyst Review & Recommendations
Industrial robotics is entering a scale-up phase where subscription financing, edge-AI intelligence, and human-robot collaboration redefine factory economics. Vendors that pair flexible hardware with data-rich service layers will outpace pure-play hardware rivals. For new entrants, lightweight cobots and industry-specific application kits offer quick traction. Established players should deepen cybersecurity capabilities and circular-economy design to align with tightening ESG benchmarks. Overall, sustained double-digit market growth remains likely as automation matures from cost-saving tool to strategic enabler of resilient, sustainable manufacturing






