Market Overview
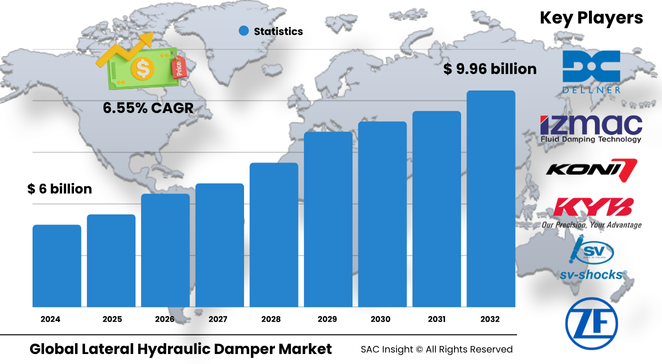
The global lateral hydraulic damper market size is valued at about US$ 6 billion in 2024 and is projected to climb to roughly US$ 9.96 billion by 2032, reflecting an average 6.55 % CAGR over the 2025-2032 forecast window. First-hand industry insights credit three main engines for this market growth: accelerating upgrades of subway and high-speed rail networks, rising retrofits of rolling stock with smart suspension packages, and steady demand from construction machinery that must meet stricter vibration-control rules. SAC Insight's deep market evaluation shows the United States lateral hydraulic damper market alone could approach US$ 1.9 billion by 2032 as transport agencies modernize commuter fleets and expand light-rail corridors.
Summary of Market Trends & Drivers
• Urban transit authorities are specifying adaptive dampers that pair hydraulic cartridges with IoT sensors, enabling predictive maintenance and smoother rides.
• Lightweight alloys and composite seals are cutting component mass by up to 15 %, improving energy efficiency for rolling stock and heavy equipment.
• Growing seismic design requirements in Asia and Latin America are pushing construction firms to install lateral dampers in bridges and high-rise frames, opening a fresh revenue stream.
Key Market Players
Industry leadership rests with a diverse mix of rail specialists and motion-control veterans. ITT KONI, ZF Friedrichshafen, and KYB supply high-capacity dampers to flagship high-speed rail programs, while Dellner Dampers and Suomen Vaimennin carve out niches in customized retrofit kits. Alstom Dispen and CRRC integrate in-house damper lines into turnkey rolling-stock platforms, whereas Indian player Escorts and China’s Zhejiang Yonggui Electric Equipment focus on cost-optimized units for emerging markets. Competitive dynamics pivot on sensor integration, service coverage, and long-term maintenance contracts rather than one-off unit sales — a shift that favors companies with global aftermarket networks.
Key Takeaways
• Current global market size (2024): about USD$ 6 billion
• Projected global market size (2032): about USD$ 9.96 billion at a 6.55 % CAGR
• North America captures roughly 35 % market share, with the United States set to top USD$ 1.9 billion by 2032
• Primary suspension units remain the volume leader, yet secondary suspension dampers are the fastest-growing slice thanks to premium ride-comfort upgrades
• Active and smart dampers already account for nearly 20 % of new orders and are expected to double their share by 2030
Market Dynamics
Drivers
• Rapid electrification and expansion of metro and high-speed rail corridors in Asia and Europe require advanced lateral control for passenger comfort and track safety.
• Construction codes mandating vibration mitigation in seismic zones stimulate damper adoption in bridges, stadiums, and high-rise buildings.
Restraints
• High upfront unit cost, complex installation, and periodic oil-seal maintenance can delay adoption among cost-sensitive fleet operators.
• Supply chain tightness for precision cylinders and high-grade elastomers can extend lead times for large rail orders.
Opportunities
• Integration of smart sensors and cloud analytics offers service providers a recurring revenue model through condition-based maintenance contracts.
• Hybrid hydraulic-magnetorheological designs promise weight savings and faster response, creating scope for premium pricing.
Challenges
• Continual compliance with differing regional safety and environmental standards raises engineering and certification costs.
• Smaller manufacturers struggle to fund R&D needed for active damping technologies, risking market share erosion as digital systems proliferate.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific posts the quickest percentage gains on the back of aggressive metro build-outs in China, India, and Southeast Asia, while North America maintains the largest revenue base owing to legacy network overhaul programs. Europe follows closely, driven by stringent ride-comfort norms and green-transport incentives.
• North America – Mature market with strong aftermarket demand and steady high-speed rail initiatives.
• Europe – High adoption of smart dampers supported by cross-border rail harmonization projects.
• Asia Pacific – Fastest growth as megacities expand metro lines and earthquake-prone regions add structural dampers.
• Latin America – Rising investment in light-rail and seismic retrofits lifts future demand.
• Middle East & Africa – Select high-speed and urban tram projects underpin a modest but rising opportunity pool.
Segmentation Analysis
By Type
• Primary Suspension – Workhorse class for axle-to-bogie damping.
Primary units absorb track-level shocks, safeguarding wheelsets at speeds above 250 km/h, and therefore command the bulk of installed base.
• Secondary Suspension – Passenger-comfort focus.
Mounted between bogie frame and car body, these dampers cut lateral sway and noise; demand is surging on premium commuter trains and night-sleeper coaches.
By Product Design
• Single-tube Dampers – Compact and cost-efficient.
Preferred for retrofit projects and low-floor trams where space is tight.
• Double-tube Dampers – Higher oil volume, better heat dissipation.
Chosen for long-distance locomotives and construction equipment that face heavy lateral loads.
• Variable Damping Dampers – Electronically adjustable orifice.
Allow on-the-fly stiffness tuning, extending service intervals and improving ride quality under variable load.
• Adjustable Dampers – Manual or semi-active settings.
Offer fleet operators flexibility to fine-tune performance without full sensor suites.
• Fixed Dampers – Simple, reliable baseline.
Continue to serve cost-sensitive freight cars and light industrial vehicles.
By Application
• Railway – Core demand engine.
Roughly 45 % of total revenue stems from passenger and freight railcars, where tighter safety rules drive replacement cycles.
Rail operators replace aging dampers every six to eight years to curb wheel wear and cut maintenance downtime, ensuring a consistent order pipeline.
• Subway – Fastest-growing slice.
Urban rail networks add new rolling stock annually, and vibration-sensitive tunnel environments favor premium dampers.
Subway contracts often bundle long-term service agreements, giving manufacturers predictable aftermarket cash flow.
• Bus – Niche but growing use for articulated and electric buses seeking car-like ride quality.
OEM partnerships with chassis builders enable direct integration during assembly.
Bus makers use lateral dampers chiefly on articulated joints and low-floor modules to control oscillation on sharp turns.
• Others – Includes monorail, trams, heavy construction machinery, and seismic building retrofits.
Each niche values customized stroke lengths and mounting brackets.
These applications diversify revenue, insulating suppliers against cyclicality in rail procurement budgets.
By End User
• Automotive and Rolling Stock OEMs
• Construction and Infrastructure Contractors
• Aerospace and Heavy-Industrial Equipment Manufacturers
• Energy and Mining Operators
By Sales Channel
• Direct Sales to OEMs
• Distributor Sales for aftermarket fleets
• Online Retail for small-batch industrial orders
• Value-added Resellers offering installation and calibration services
Industry Developments & Instances
• July 2022 – A major European supplier launched an IoT-enabled damper with cloud diagnostics, cutting unscheduled maintenance by an estimated 20 %.
• March 2023 – An Asian rail integrator awarded a multi-year deal for active secondary suspension dampers across a 200-train metro expansion.
• September 2024 – A construction consortium selected custom lateral dampers for a suspension bridge in a high seismic zone, highlighting cross-sector adoption.
• May 2025 – A partnership between a damper maker and a sensor start-up introduced retrofit kits that upgrade legacy hydraulic units to smart status within two hours.
Facts & Figures
• Active or smart dampers are expected to hold over 35 % market share by 2032, up from just under 20 % today.
• Secondary suspension units account for close to 60 % of new high-speed train orders placed in 2024.
• Predictive maintenance enabled by vibration sensors can lower life-cycle costs by 12 % compared with time-based schedules.
• Composite piston rods reduce damper weight by up to 1.5 kg per unit, translating into annual energy savings of roughly 40 MWh for a 16-car trainset.
• Average replacement cycle for railway dampers is six to eight years, creating a predictable aftermarket of nearly 400,000 units per year by 2030.
Analyst Review & Recommendations
Market analysis underscores a pivot from static, price-driven procurement to holistic performance contracts that bundle smart dampers with cloud analytics. Suppliers that pair lightweight materials with plug-and-play sensor modules will outpace baseline market trends. To capture emerging opportunities, manufacturers should prioritize modular designs that fit both rolling stock and civil-engineering projects, invest in regional service hubs to shorten overhaul turnaround, and pursue joint R&D programs that accelerate active damping breakthroughs while meeting evolving compliance norms."






